Quick Start Highlight
Semax is a synthetic peptide derived from a portion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH 4-10), modified with a Pro-Gly-Pro sequence to increase stability and brain penetration. Unlike typical ACTH fragments, Semax does not affect cortisol levels—but instead works as a neuroprotective and nootropic agent.
It was first developed by Russian scientists in the 1980s as a treatment for ischemic stroke, cognitive decline, and brain injury. It’s been approved for clinical use in Russia and Ukraine for decades, but in the U.S., it’s sold for research purposes only.
What sets Semax apart from most peptides or supplements is its ability to target brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) pathways and modulate dopamine and serotonin, making it a unique cognitive enhancer without stimulant effects.
Benefits of Semax
Semax isn’t your typical “smart peptide” Instead of jacking up energy or stimulating your nervous system, it works behind the scenes—enhancing neuroplasticity, protecting your brain from stress, and optimizing performance when it matters most.
Here’s what beginners and biohackers alike report when using Semax:
1. Improved Focus and Mental Clarity
Semax helps increase dopaminergic activity in the prefrontal cortex, the area responsible for working memory and executive function. This translates to:
Sharper concentration
Less mental fatigue
More productive deep work sessions
Many users report a “clean focus” effect—without overstimulation or emotional blunting like Adderall or modafinil.
2. Enhanced Memory and Learning
By increasing BDNF expression, Semax promotes synaptic plasticity and long-term potentiation (LTP)—the neural mechanisms behind learning and memory formation.
Easier recall
Faster learning
Improved retention during study or high-pressure situations
3. Mood and Anxiety Support
Because Semax indirectly modulates serotonin and dopamine, it may improve mood, motivation, and resilience to stress. It’s been studied as a treatment for depressive symptoms, without the sedative or flattening effects of SSRIs.
Better stress response
More emotional stability
Less burnout
4. Neuroprotection and Brain Recovery
Originally used to treat stroke and traumatic brain injury, Semax promotes neurogenesis, increases cerebral blood flow, and helps protect neurons under oxidative stress.
Recovery from concussion or neural inflammation
Support for cognitive decline or brain fog
Potential benefit for overtrained athletes or chronic stress
5. Fatigue Resistance and Performance Under Stress
Semax has been used by cosmonauts, military personnel, and Olympic athletes to maintain cognitive performance in extreme environments—like high stress, low sleep, and sensory overload.
Sustained cognition under fatigue
Faster rebound from mental exhaustion
Adaptive resilience during travel or demanding projects
How Does Semax Work?
Semax works on multiple neurological pathways, but its primary mechanisms include:
1. BDNF Upregulation
Semax stimulates the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that promotes:
Neuronal growth and repair
Synaptic plasticity (learning and memory)
Cognitive resilience under stress or aging
BDNF is considered one of the most important molecules for brain performance, and Semax has been shown to significantly increase its expression in animal models.
2. Dopamine and Serotonin Modulation
Semax modulates dopaminergic and serotonergic signaling, helping to regulate:
Motivation
Focus and alertness
Mood and emotional stability
It may enhance mental clarity without overstimulating the central nervous system—making it appealing to those who don’t tolerate caffeine or amphetamine-based nootropics.
3. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
Semax reduces oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, particularly in ischemic brain conditions or periods of extreme mental fatigue. This is especially helpful during overtraining, burnout, or sleep deprivation.
Potential Side Effects
Common Side Effects
Mild nasal irritation – Slight burning, dryness, or congestion can occur with frequent intranasal use.
Headache – Usually related to higher doses or dehydration; often resolves with proper hydration or dosage adjustment.
Restlessness or overstimulation – Rare, but possible if dosing is too high or taken too close to bedtime.
Rare or Reported Effects
Mood fluctuations – In some users, dopamine or serotonin modulation may trigger brief emotional swings
Temporary increase in blood pressure – Seen in very high doses or when stacked with other stimulants.
Sleep disruption – Rare, but those sensitive to dopamine shifts may notice lighter sleep patterns.
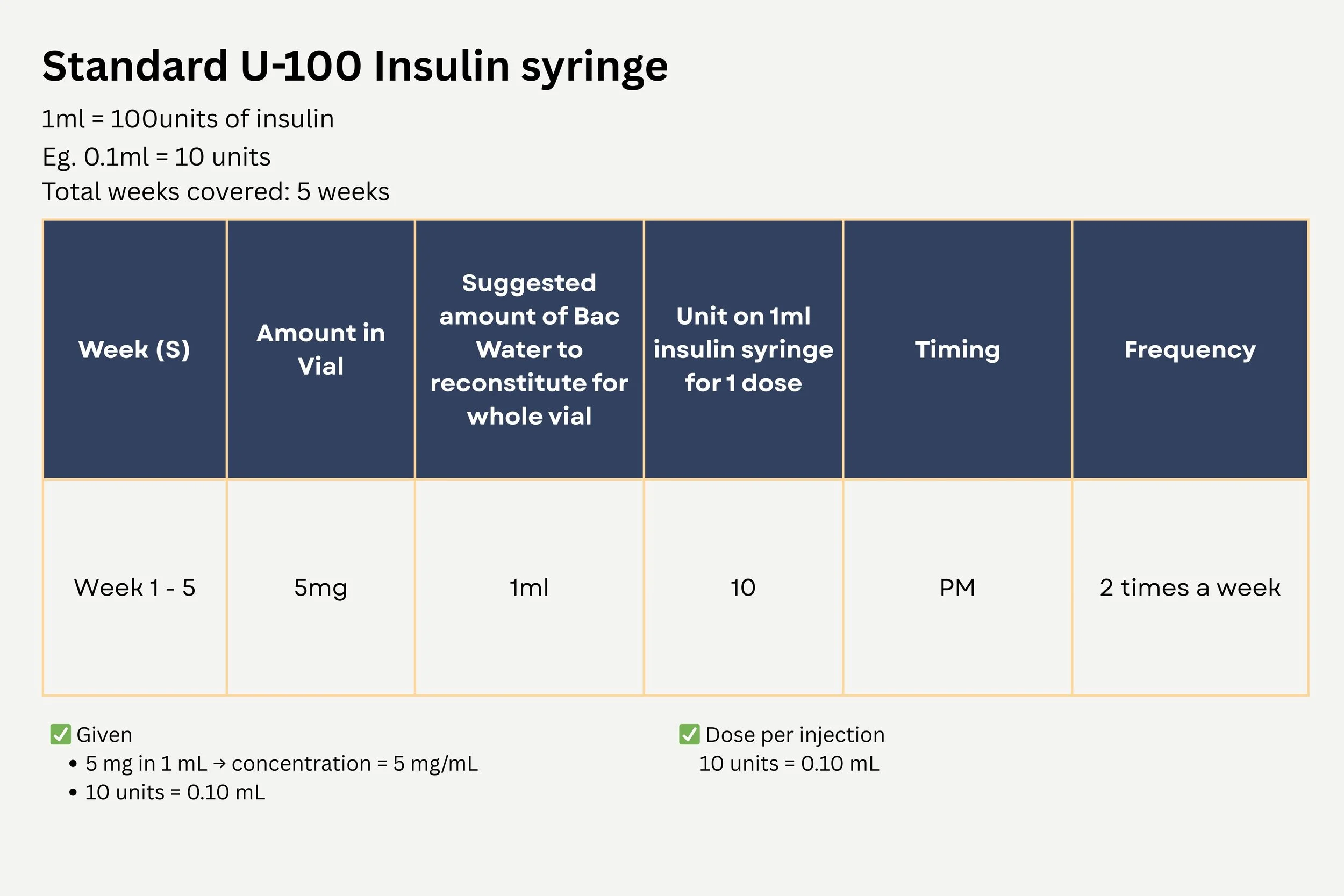
Dosing & Reconstitution Guide
Educational guide for reconstitution and weekly dosing